Laryngoscopy: A Comprehensive Guide to Tracheal Intubation in Medicine
Introduction
Laryngoscopy is a crucial medical procedure that allows healthcare professionals to visualize the larynx and perform tracheal intubation. This article provides a comprehensive guide to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation, explaining the techniques, equipment used, and their significance in the field of medicine.
1. Overview of Laryngoscopy
Laryngoscopy is a medical procedure used to examine the larynx, which houses the vocal cords. It allows physicians to assess the airway and perform tracheal intubation, a procedure in which a tube is inserted into the trachea to secure the airway and facilitate mechanical ventilation.
2. Types of Laryngoscopy
2.1 Direct Laryngoscopy
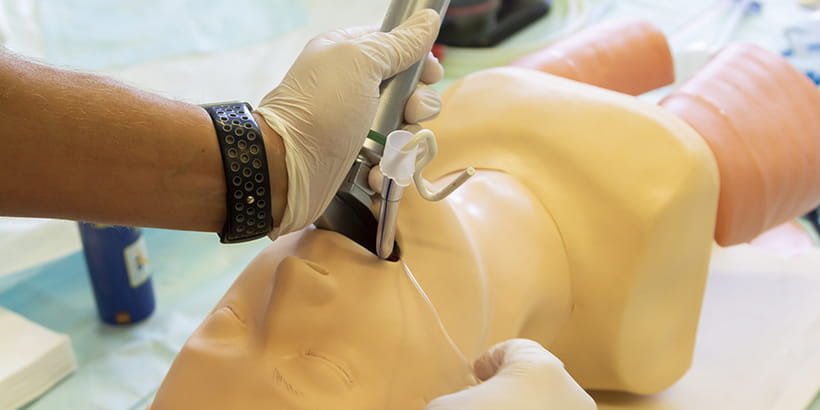
Direct laryngoscopy involves the use of a laryngoscope, a specialized instrument, to directly visualize the larynx. The laryngoscope is inserted into the patient’s mouth and used to lift the epiglottis, providing a clear view of the vocal cords.
2.2 Indirect Laryngoscopy
Indirect laryngoscopy utilizes techniques that do not involve direct visualization of the larynx. It typically involves the use of mirrors or flexible scopes to indirectly visualize the vocal cords. Indirect laryngoscopy is often used in situations where direct laryngoscopy is challenging or not feasible.
3. Laryngoscope and Its Components
The laryngoscope consists of a handle and a blade. The blade is available in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific patient populations and clinical scenarios. Commonly used blade types include Macintosh, Miller, and D-BLADE.Odynophagia after celebrating Independence Day
4. Preparing for Laryngoscopy
4.1 Patient Evaluation
Before performing laryngoscopy, a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, airway assessment, and relevant imaging studies is essential. This evaluation helps identify any potential difficulties or complications that may arise during the procedure.
4.2 Numbing the Throat
To minimize discomfort during laryngoscopy, the patient’s throat is often numbed with a local anesthetic spray or gel. This helps reduce the gag reflex and allows for smoother insertion of the laryngoscope.
4.3 Positioning the Patient
Proper patient positioning is crucial for successful laryngoscopy. The patient’s head and neck should be aligned, and the neck extended to achieve optimal visualization of the larynx. Various positioning aids, such as pillows or pads, can be used to assist in achieving the desired position.
5. Performing Laryngoscopy
5.1 Inserting the Laryngoscope
Once the patient is appropriately positioned, the laryngoscope is inserted into the mouth, and the blade is gently placed in the vallecula (a depression between the base of the tongue and epiglottis). Care should be taken to avoid dental trauma or injury to the soft tissues of the mouth.
5.2 Visualizing the Larynx
With the laryngoscope in place, the operator lifts the blade, elevating the epiglottis and exposing the larynx. This provides a clear view of the vocal cords and allows for assessment of their movement, color, and any signs of pathology.
5.3 Intubation Techniques
Tracheal intubation can be performed during laryngoscopy using various techniques. The endotracheal tube (ETT) is carefully guided through the vocal cords and advanced into the trachea. Confirmation of correct tube placement is crucial and is typically achieved by observing chest rise, breath sounds, and waveform capnography.
6. Complications and Safety Measures
6.1 Potential Complications
Laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation are associated with potential complications, including dental injury, mucosal trauma, vocal cord damage, and hypoxia. Recognizing these complications promptly and taking appropriate measures can help minimize their impact.
6.2 Prevention and Management
To reduce the risk of complications, healthcare professionals should undergo proper training and maintain proficiency in laryngoscopy techniques. Additionally, utilizing adjunct devices, such as video laryngoscopes or fiberoptic bronchoscopes, can aid in difficult airway management and minimize complications.
7. Advancements in Laryngoscopy
7.1 Video Laryngoscopy
Video laryngoscopy involves the use of a camera and a monitor to visualize the larynx. This technique provides a magnified and enhanced view of the vocal cords, making it useful in challenging airway scenarios or when direct laryngoscopy is unsuccessful.
7.2 Fiberoptic Laryngoscopy
Fiberoptic laryngoscopy utilizes a flexible scope with a fiberoptic bundle that allows indirect visualization of the larynx. This technique is particularly valuable in patients with difficult airways or those who require awake intubation.
8. Importance of Tracheal Intubation
Tracheal intubation plays a vital role in many medical settings. It ensures airway patency, facilitates mechanical ventilation, and allows for the administration of anesthesia. Properly securing the airway through tracheal intubation is critical for patient safety and optimal clinical outcomes.
Conclusion
Laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation are essential procedures in medicine. They enable healthcare professionals to visualize the larynx and secure the airway. By understanding the techniques, equipment, and potential complications associated with laryngoscopy, healthcare providers can ensure safe and effective patient care.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What is the purpose of laryngoscopy?
- Laryngoscopy allows visualization of the larynx and facilitates tracheal intubation, securing the airway for various medical procedures.
- Are there any risks associated with laryngoscopy?
- Yes, potential complications of laryngoscopy include dental injury, mucosal trauma, vocal cord damage, and hypoxia. However, these can be minimized with proper training and precautions.
- What are the advancements in laryngoscopy techniques?
- Video laryngoscopy and fiberoptic laryngoscopy are two significant advancements that aid in difficult airway management and provide enhanced visualization of the larynx.
- Why is tracheal intubation important in medicine?
- Tracheal intubation ensures airway patency, facilitates mechanical ventilation, and allows for the administration of anesthesia, making it essential for patient care.
- How can healthcare providers improve their proficiency in laryngoscopy?
- Healthcare providers should undergo proper training, stay updated on advancements, and regularly practice laryngoscopy techniques to maintain proficiency.