How Are Viruses Different from Bacteria Apex?
Introduction
In the world of microscopic organisms, viruses and bacteria hold significant importance. Both have the potential to impact human health, but they differ in various aspects. Understanding the differences between viruses and bacteria is crucial for effective medical treatments and preventive measures. In this article, we will explore the distinctions between these two types of microorganisms and shed light on how they affect us differently.
Definition and Characteristics of Viruses
Viruses are tiny infectious agents that consist of genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protein coat. They are considered non-living entities as they lack the ability to replicate or perform metabolic activities on their own. Viruses rely on host cells to reproduce and survive. They have diverse shapes, ranging from complex geometrical structures to simple shapes like rods or spheres.
Definition and Characteristics of Bacteria
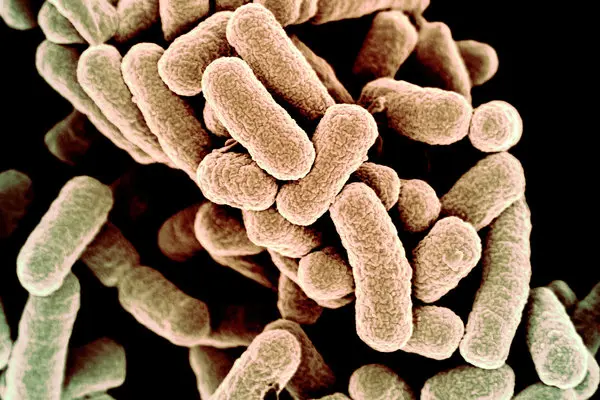
Bacteria, on the other hand, are single-celled microorganisms that can survive and reproduce independently. They have a prokaryotic cellular structure, lacking a distinct nucleus. Bacteria come in various shapes such as cocci (spherical), bacilli (rod-shaped), and spirilla (spiral-shaped). They have their own genetic material and are capable of metabolic activities.
Structure and Reproduction
Viruses have a relatively simple structure compared to bacteria. They consist of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid. Some viruses also have an outer envelope derived from the host cell’s membrane. Viruses cannot reproduce on their own and must infect a host cell to hijack its cellular machinery and replicate.
Bacteria, on the other hand, have a more complex cellular structure. They possess a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, and various internal organelles. Bacteria reproduce through binary fission, a process where a single bacterium divides into two identical daughter cells.
Mode of Infection
Viruses primarily infect living organisms by attaching to specific host cells and injecting their genetic material into them. The infected host cell then follows the instructions encoded in the viral DNA or RNA, leading to the production of new viral particles. This process often causes damage to the host cell.
Bacterial infections occur when bacteria invade and multiply within host tissues. They can affect various parts of the body, such as the respiratory tract, urinary tract, or skin. Bacteria can also release toxins that harm the host.
Read Also
Effect on Human Health
Both viruses and bacteria can cause diseases in humans. However, the impact and nature of the diseases differ. Viral infections are responsible for numerous diseases, including the common cold, influenza, measles, and HIV/AIDS. Viruses are also associated with serious outbreaks, such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
Bacterial infections can lead to a wide range of illnesses, such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and food poisoning. Some bacteria are beneficial and play important roles in the human body, such as aiding digestion or producing essential vitamins.
Medical Treatments
The treatment approaches for viral and bacterial infections vary due to the differences in their structures and replication mechanisms. Antibiotics are effective against bacteria but are ineffective against viruses. Antiviral drugs specifically target viral infections and inhibit their replication. Vaccines are another important tool in preventing viral infections by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight off viruses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, viruses and bacteria are distinct types of microorganisms with different structures, modes of infection, and effects on human health. Viruses lack cellular structure and rely on host cells for replication, while bacteria are independent single-celled organisms. Understanding these differences enables medical professionals to develop targeted treatments and preventive measures to combat viral and bacterial infections effectively.
FAQs
- Q: Can antibiotics cure viral infections? A: No, antibiotics are ineffective against viral infections. They only work against bacterial infections.
- Q: Are all bacteria harmful? A: No, some bacteria are beneficial and necessary for various bodily functions.
- Q: How do viruses spread? A: Viruses can spread through respiratory droplets, direct contact, or contaminated surfaces.
- Q: Can bacterial infections be prevented? A: Yes, practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing, can help prevent bacterial infections.
- Q: Are all viruses harmful to humans? A: No, not all viruses cause diseases in humans. Some viruses are harmless or even beneficial.