NASA’s Moon Exploration: Unveiling the Wonders of Our Celestial Neighbor
Embarking on a celestial journey, NASA, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, has been at the forefront of unraveling the mysteries of our vast universe. One of their most iconic endeavors is the exploration of the Moon, a celestial body that has captivated humanity for centuries. In this beginner’s guide, we will delve into the fascinating world of NASA’s Moon exploration, from the historic moon landing to ongoing missions and the promise of the lunar frontier.
The Historic Moon Landing:
Transitioning back to July 20, 1969, marks a pivotal moment in human history – the day when NASA’s Apollo 11 mission successfully landed humans on the Moon. Astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin, under the command of Michael Collins, etched their names in the annals of space exploration. The world collectively held its breath as Armstrong took the first steps, proclaiming, “That’s one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind.”
Transitioning to the Active Moon Landing:
Fast forward to the present, and NASA’s commitment to lunar exploration remains unwavering. With Artemis, the new lunar program, the agency plans to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by the mid-2020s. The Artemis program, named after the twin sister of Apollo in Greek mythology, aims to establish sustainable human presence on the Moon, serving as a stepping stone for future missions to Mars and beyond.
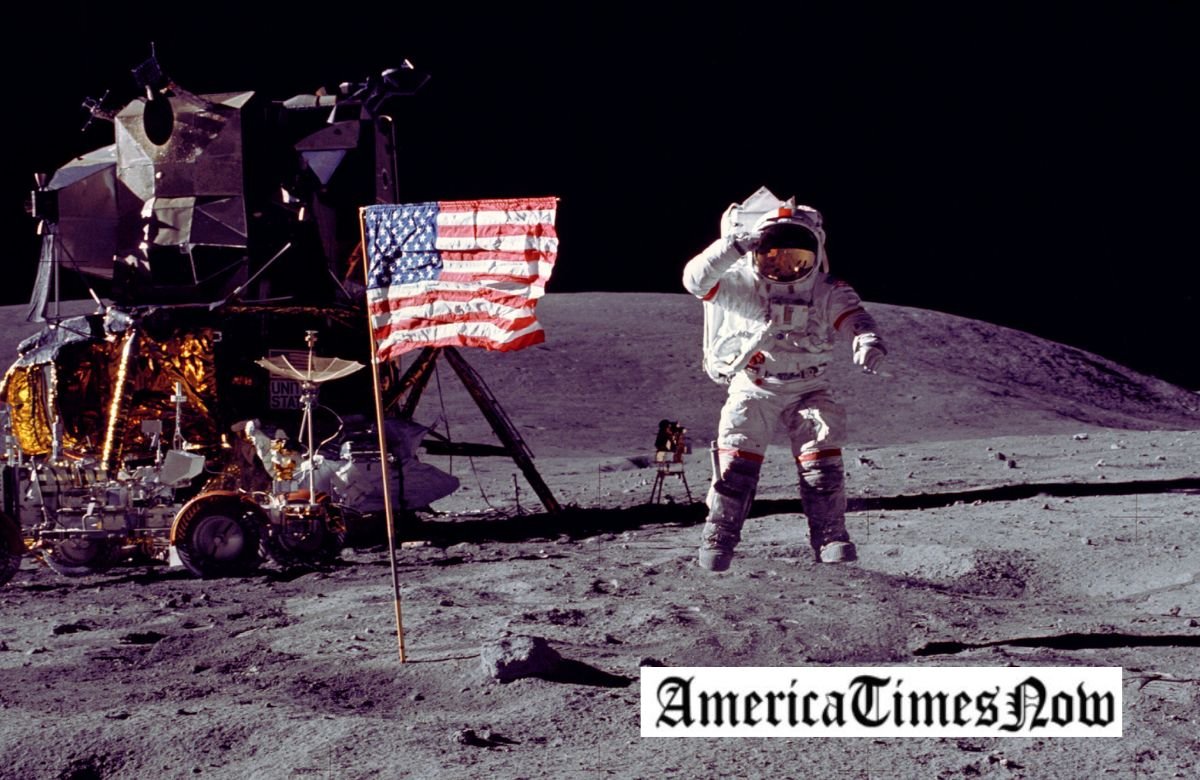

Exploring the Lunar Surface:
Transitioning to the lunar surface, one cannot help but marvel at the diverse landscapes and geological features that await exploration. From vast plains to towering mountains and deep craters, the Moon offers a unique canvas for scientific investigation. NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) has been diligently mapping the lunar terrain, providing crucial data for future missions and uncovering hidden details about the Moon’s composition.
Transitioning to Lunar Water Ice:
Intriguingly, recent discoveries have hinted at the presence of water ice on the Moon. Scientists believe that these ice deposits, particularly in permanently shadowed regions, could serve as a valuable resource for future lunar missions. Transitioning from Earth to the Moon could become more sustainable, with water acting as a crucial component for life support and fuel production.
Ongoing Lunar Missions:
Transitioning to the ongoing lunar missions, NASA has been deploying a fleet of robotic explorers to investigate various aspects of the Moon. The Lunar Gateway, a space station in lunar orbit, will serve as a crucial hub for future missions, enabling sustained human presence and facilitating scientific research. The Gateway will act as a staging point for lunar landers, providing a gateway for exploration deeper into our solar system.
Transitioning to International Collaboration:
NASA’s lunar exploration efforts extend beyond national borders, fostering international collaboration. The Artemis Accords, a set of principles for responsible lunar exploration, have garnered support from various countries. This collaborative approach not only enhances the scientific value of lunar exploration but also paves the way for a shared human future beyond Earth.
Transitioning to Moon Myths and Mysteries: Beyond the scientific endeavors, the Moon has been a source of inspiration, myths, and mysteries throughout human history. Transitioning to ancient cultures and civilizations, the Moon often held significant symbolic and cultural importance. From lunar deities to folklore, the Moon’s influence on human imagination has been profound.
Future Prospects and Lunar Dreams:
As we transition to the future, the Moon remains a beacon of inspiration for dreamers and visionaries. The promise of establishing a sustainable human presence, mining lunar resources, and unraveling the remaining mysteries continues to drive NASA’s lunar exploration efforts. The Moon is not just a celestial neighbor; it’s a stepping stone, a testament to human curiosity and the unquenchable thirst for exploration.
Conclusion:
In this beginner’s guide to NASA’s Moon exploration, we’ve taken a journey from the historic Apollo 11 mission to the ongoing Artemis program. The Moon, with its diverse landscapes and scientific mysteries, beckons humanity to explore and understand our celestial neighbor. As we look to the future, the Moon stands as a symbol of human ingenuity, collaboration, and the unwavering pursuit of knowledge in the vast expanse of space. So, let your imagination soar, and join NASA on the thrilling adventure of lunar exploration!